PHOTOGRAPHS FROM THE INITIAL STAGES OF THE STUDY |
 |
 |
|
| 0.1
The examination of two degraded oligonucleotid samples obtained from Gebze Marmara Research Center. |
0.2
Burkitt lymphoma |
|
FIRST GROUP OF PHOTOGRAPHS: Liquid crystal features of the Uracil base
|
 |
 |
 |
| 1.01
The cultures of uracil in water: formation of cellulose vesicles |
1.02
The cultures of uracil in water: formation of cellulose vesicles |
1.03
The cultures of uracil in water: formation of cellulose vesicles |
 |
 |
 |
1.2
The cultures of uracil in water
|
1.3
The cultures of uracil in water |
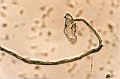
1.4
The cultures of uracil in water: formation of fibrilles |
 |
 |
 |
| 1.5
The cultures of uracil in water: formation of fibrilles |
1.6
Mobile protozoon formations which are developed from the cultures of the uracil base with water and sugar. |
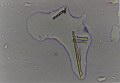
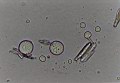
1.7
The cultures of uracil and water: formations resembling grana and thylakoids in chloroplasts |
 |
 |
|
| 1.8 The melted form of the uracil base in water: appearance of lyotropic liquid crystals and prochloron series. |
1.9 A detailed view of the
prochlorons seen in Figure 1.8 (see the cellulose vesicles within these
prochlorons) |
|
SECOND GROUP OF PHOTOGRAPHS: Formation of cellulose from the Uracil base |
 |
 |
 |
| 2.1
The cultures of uracil in water using the suspension technique: formation of (reticular) cellulose vesicles |
2.2 The cultures of uracil in water using the suspension technique: formation of (reticular) cellulose vesicles |
2.3
Formation of a fibrille from the uracil base |
 |
 |
 |
| 2.4
The cultures of uracil in water using the suspension technique: formation of nodules, fibrilles and reticular cellulose vesicles |
2.5
When the adenine base is added to the cultures of uracil and water, uracil's ability of producing cellulose enhances. Furthermore, chains of hypha and ascus-like cellulose vesicles appear in the medium. |
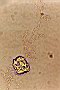
2.6
The cultures of uracil in water: formation of cellulose vesicles and a prochloron. |
 |
 |
 |
| 2.7 The cultures of uracil in water: the formation of cellulose vesicles from a fibrille. These vesicles highly resemble to the appearances of the so-called pigments, which are believed to be formed from melanosit cells in human brain. |
2.8 Cellulose formation in the plasmal monolayer culture of the uracil base |
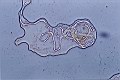
2.9 The cultures of uracil in water using the suspension technique: The formation of cellulose vesicles, which develop from a nodule |
 |
 |
 |
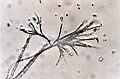
| 2.10 When the adenine base is added to the cultures of uracil and water, uracil's ability of producing cellulose enhances. |
2.11 A detailed view of the Figure 2.10. |
2.12 Cultures of uracil in water with additional tobacco extract: the formation of cellulose fibrilles and cellulose vesicles |
 |
 |
|
| 2.13 Various formations
seen in the cultures of uracil in water: Crystals, prochloron and cellulose
vesicles |
2.14 Various formations
seen in the cultures of uracil in water: Crystals, prochloron and cellulose
vesicles |
|
THIRD GROUP OF PHOTOGRAPHS: The appearance of the uracil base in plants
|
 |
 |
 |
| 3.1
Prechloroplastic developments |
3.2
The examination of bean roots in water: see the accumulation of uracil liquid crystals, which develop from the cell wall |
3.3
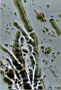
The juice of pot grown lily stems: Fibrilles developing from the uracil crystals |
 |
 |
|
| 3.4
The juice of pot grown lily stems: Nodules developing from the uracil crystals |
3.5
The juice of pot grown lily stems: Photosynthetic membranes developing from the uracil crystals |
|
FOURTH GROUP OF PHOTOGRAPHS: The appearance of the uracil base in some of the histopathology preparations
|
 |
 |
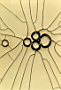 |
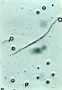
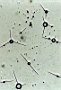
| 4.1
Blood samples taken from a patient who was diagnosed as cancer of bowels: see the prochlorons and a cellulose fibrille. |
4.2
Blood samples taken from a patient who was diagnosed as cancer of bowels: see the prochlorons and hypha formations, which develop from these prochlorons. |
4.3
Blood samples taken from a patient who was diagnosed as cancer of bowels: see the prochlorons and hypha formations, which develop from these prochlorons. |
 |
 |
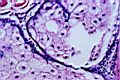 |
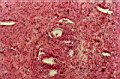
| 4.4
Blood samples taken from a patient who was diagnosed as cancer of bowels: see the development of hypha and cellulose micelles from prochlorons. |
4.5
A preparation from a patient who was diagnosed as cancer of prostate: see the fibrille, nodule and reticular cellulose vesicles. |
4.6
A preparation from a patient who was diagnosed as thyroid hypertrophy: see the fibrille, nodule and reticular cellulose vesicles. |
 |
 |
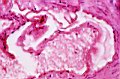 |
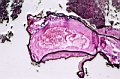
| 4.7
Fibril and cellulose vesicles in a BSE preparation. |
4.8
Prochlorons (see in black colour) and cellulose vesicles narrowing or blocking the inner surface of the brain arteries of a patient. |
4.9
A detailed view of the Figure 4.8: see a better view of the cellulose vesicles. |
 |
 |
|
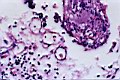
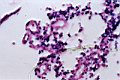
| 4.10
A preparation from a patient's brain who was diagnosed as alzheimer: see the nodules and reticular cellulose vesicles, which develop from uracil crystals. |
4.11
A preparation from a patient's brain who was diagnosed as alzheimer: see the nodules and a cellulose fibrille, which develop from uracil crystals. |
|